China (mainland) - World Nuclear Performance Report
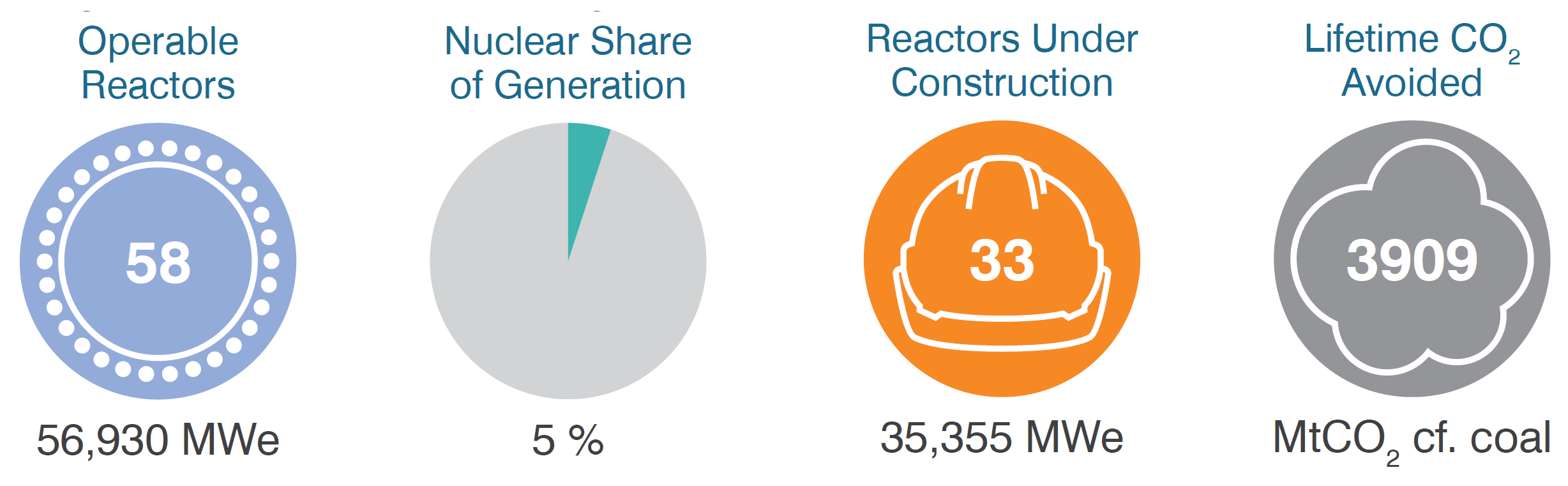
Mainland China has 58 operable reactors with a total capacity of 57 GWe, primarily at sites along its southeast coastline. It also had 32 reactors under construction as of 31 July 2025, totalling 34 GWe.
In October 2024 the country’s first CAP1400 reactor was connected to the grid. The CAP1400 is an enlarged version of the Westinghouse AP1000 PWR. In November 2024 unit 1 of CNNC’s Zhangzhou project in Fujian province was connected to the grid. It is the first of four Hualong One reactors under construction at the site. Six reactors commenced construction during 2024 (Zhangzhou 3, Lianjiang 2, Xudabao 2, Shidaowan 1, Ningde 5 and Zhangzhou 4). As of 31 July, construction of a further three units has commenced in 2025 (Lufeng 1, Shidaowan 2, Taipingling 3).
In August 2024 China’s State Council approved five nuclear projects with a total of 11 reactors: Xuwei Phase I, Lufeng Phase I, Zhaoyuan Phase I, San'ao Phase II and Bailong Phase I – with a total of 11 reactors. Groundworks for unit 1 at Bailong began in January 2025. In April 2025 the Council approved a further five projects comprising 10 reactors – Fangchenggang Phase III, Haiyang Phase III, Sanmen Phase III, Taishan Phase II and Xiapu Phase I.
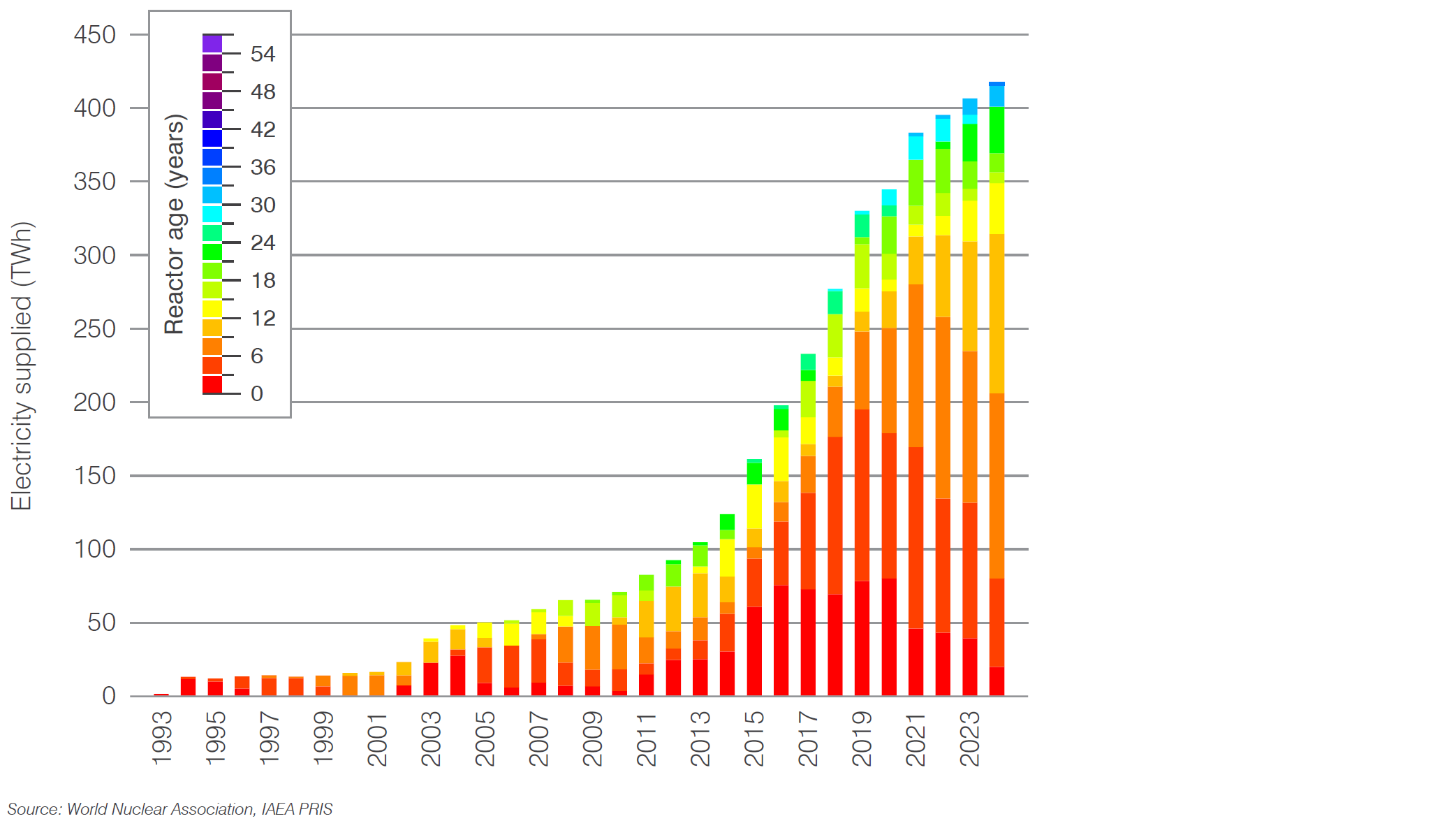
Electricity generation by age of reactor